U.S. climate outlook for June 2024
I know I sound like a broken record, but May was again a warmer-than-normal month for large parts of the United States, particularly from the Rockies eastward. In fact, the temperature pattern was quite similar to March, with near- and below-normal temperatures generally observed from the Rockies to the West Coast. And not surprisingly, temperatures this spring were also above average east of the Rockies and normal to below normal to the west. Beneficial rains fell across parts of the central and eastern parts of the nation during May, with the amount of drought decreasing in these regions.
With summer beginning, will temperatures remain above average? Will beneficial rains continue to fall in the important growing regions of the nation? This is what NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center (CPC) thinks will happen during June.
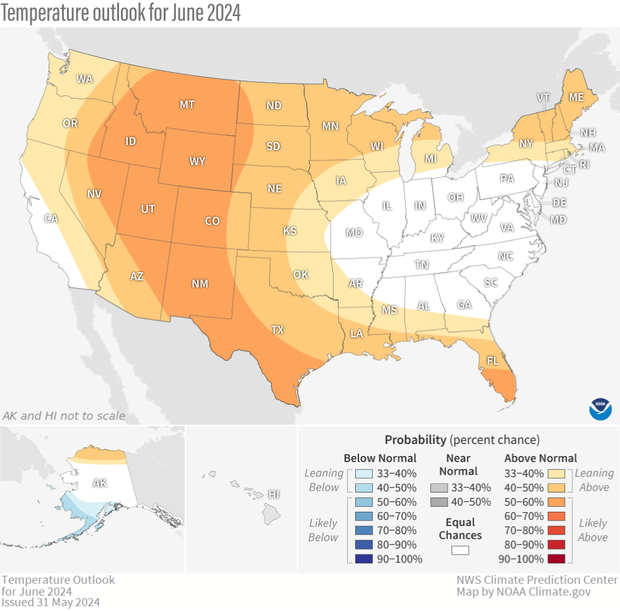
The U.S. temperature outlook for June 2024, showing where the average temperature is favored to be much warmer than average (orange and red), near average (gray), or much cooler than average (blues). Darker colors mean higher chances, not more extreme temperatures. White areas mean that there are equal chances for a warm, cool, or near-average June. Much warmer or much cooler than average means "in the upper or lower third" of June temperatures from 1991-2020. For more details on how to interpret these maps, read our explainer Understanding NOAA's monthly climate outlooks. Text-only forecast for Hawaii available from NOAA Climate Prediction Center.
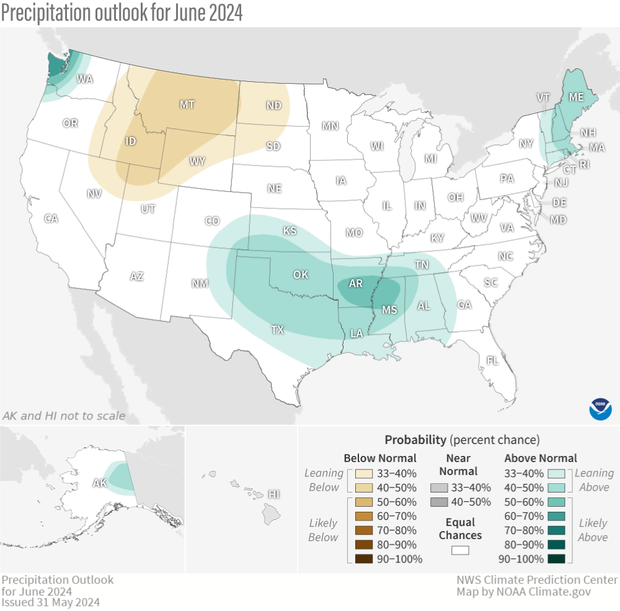
On May 31, CPC released its updated monthly climate outlooks for temperature, precipitation, and drought across the United States for June 2024. The temperature outlook favors well above average temperatures across much of the central and western parts of the nation, along the Gulf Coast to Florida, around the Great Lakes, and in the Northeast, with no tilt in odds toward any category over the remainder of the country. The precipitation outlook favors well above average precipitation across parts of the south-central and southeastern U.S., western Washington, and in the Northeast, and well below average precipitation favored in the Northern Rockies and Northern Plains.
The precipitation outlook for June 2024, showing where the average precipitation (rain and snow) is favored to be much higher than average (greens), near average (gray), or much lower than average (browns). Darker colors mean higher chances, not more extreme precipitation departures. White areas mean that there are equal chances for a wet, dry, or near-average June. Much higher or much lower than average means "in the upper or lower third" of June precipitation amounts from 1991-2020. For more details on how to interpret these maps, read our explainer Understanding NOAA's monthly climate outlooks. Text-only forecast for Hawaii available from NOAA Climate Prediction Center.
In addition to drilling down into the specifics about the outlooks and their basis, I’ll also discuss the current state of drought, changes in drought during May, and changes we expect to see during June. And the broken record continues here, with my monthly reminder to the reader that the colors on the temperature and precipitation outlook maps only provide information about the most likely outcome, but other outcomes are still possible, although less likely to occur. More details about interpreting the outlooks can be found here.
The updated outlooks were produced considering the Week 1 forecast from the Weather Prediction Center (WPC), and CPC’s own Week 2 and Week 3-4 outlooks. Other tools that forecasters examined this month were longer-range forecast models such as the Global Ensemble Forecast System (GEFS), the Climate Forecast System (CFSv2), and products derived from these models. And as the transition of El Niño to neutral is imminent, El Niño was not a factor in the June outlooks. Finally, observed soil moisture was considered for these outlooks, as extremes in soil moisture (both wet and dry) can influence temperatures during the spring and summer.
Temperature outlook favors change in the pattern
The June temperature outlook favors a change from the May (and March) temperature pattern, with elevated odds for well above average temperatures across much of the western and central parts of the nation. There is more uncertainty in the East, although above-average temperatures are still favored in the Northeast and along the Gulf Coast and Florida. The region most likely to be warmer than average extends from southern Texas northward through much of the Southwest into the central and northern Rockies, where odds exceed 50%. No areas are favored to be colder than average, with equal chance odds (1/3 chance each of below-, near-, and above-average temperatures) found in the Ohio and Tennessee Valleys eastward to the Mid-Atlantic and Southeast.
Sub-seasonal model guidance (the GEFS and CFSv2 models mentioned above) favors mean ridging (where the jet stream is shifted north of normal) over the west-central country in early and mid-June. This ridging elevates odds for warmer-than-normal conditions for the first half of June for much of this area, as does dry soil moisture conditions currently observed in parts of the Pacific Northwest, northern Rockies, Southwest, and southern High Plains. Subtropical ridging along the southern tier of the U.S. supports elevated odds for above-normal temperatures for the southern Plains, along the Gulf Coast, and in the Southeast. Meanwhile, model guidance during the short and sub-seasonal range supports above-average temperatures throughout the Great Lakes and Northeast regions.
Precipitation outlook is more questionable
As is often the case, forecast coverage in the precipitation outlook is less cohesive than in the temperature outlook. The only region favored to have below-average precipitation is in the northern Rockies and northern High Plains, where the aforementioned strong ridging favored throughout most of the month should limit precipitation. The ridge does favor a downstream (farther east) trough (where the jet stream is shifted south of normal and contributes to unsettled weather) from the Southern Plains eastward into the Southeast, which elevates the odds for a wetter-than-normal June in that region.
High odds for above-average monthly precipitation is forecast for a small region in the far Pacific Northwest, where large rainfall amounts are predicted during the first week of June. Finally, forecast troughing (jet stream shifted south of normal) around the Great Lakes favors unsettled conditions downstream, resulting in a tilt in the odds in the Northeast towards above-average precipitation.
U. S. drought area decreases during May
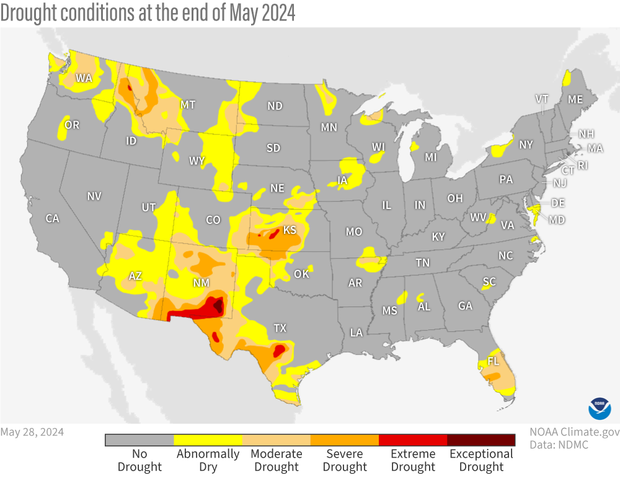
Beneficial rains across the middle and eastern parts of the nation during May resulted in the total amount of drought across the continuous United States decreasing from 18% at the end of April to about 12.5%. This is the lowest amount of drought coverage across the contiguous U. S. since spring 2020. The percent of the country in the two most intense categories (D3-D4, representing extreme and exceptional drought) remained at less than 1%, also the lowest amount since April 2020.
Drought conditions across the contiguous United States as of May 28, 2024. Extreme (red) and exceptional (dark red) drought was present in relatively small parts of New Mexico, Texas, Kansas, and Idaho, less than 1% of the country. Map by NOAA Climate.gov, based on data provided by the U.S. Drought Monitor project.
Regionally, drought improvement was recorded in most regions of the country, with significant improvement found in the northern and central Great Plains (2-3 classes). In particular, improvement over Iowa was such that none of the state was in drought at the end of May, the first time that has occurred since the end of June 2020. Drought removal also occurred over large parts of Minnesota and northeastern North Dakota. In contrast, drought degradation was more pronounced over Florida, where drought developed and worsened up to 2 classes. Some limited degradation (1-2 classes) was also recorded in southern Texas, around the Texas and Oklahoma panhandles, and in Washington state.
Drought outlook tilts toward persistence and development
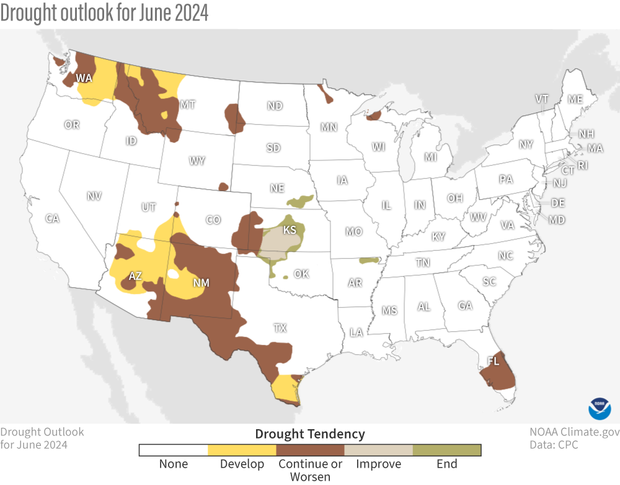
The drought outlook for June predicts drought persistence for most regions of the nation currently in drought. In addition, development is favored in significant parts in south Texas, the Southwest, and in the northern Rockies. With antecedent dryness and below-normal snowpack, drought is likely to develop in the northern Rockies, as excessive heat and below-normal rainfall is favored in much of this region, especially early in the month. Drought persistence and development in south Texas and in the Southwest is also likely, with conditions currently drier than average, and expectations of above-average temperatures as we head into the warmest time of year.
U.S. map of predicted drought changes or persistence in June 2024. Some areas of new drought are forecast to develop across parts of the northern Rockies, Southwest and southern Texas. Drought is forecast to continue or worsen across portions of Florida, the Southwest, central Great Plains and northern Rockies. Drought improvement and removal is likely across areas of Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. NOAA Climate.gov map, based on data from the Climate Prediction Center.
In contrast, drought improvement and some removal is likely in parts of Nebraska, Kansas, and Oklahoma, as favorable precipitation outlooks during the first half of June is combined with heavy rainfall that fell at the end of May.
To read the entire discussion of the monthly climate outlooks from the Climate Prediction Center, check out their website.