Coral reefs are important and productive ocean ecosystems, providing shelter and protection for diverse sea life. NOAA's latest seasonal outlook for coral bleaching shows potential for bleaching along the Pacific coast of Mexico and islands in the equatorial central Pacific Ocean.
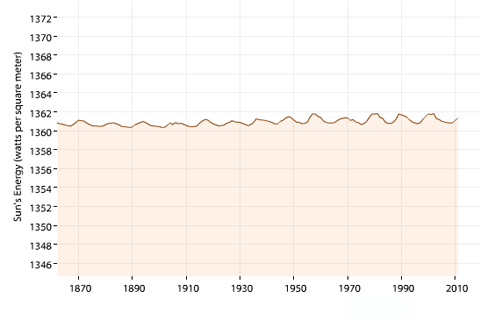
The Sun's average brightness varies over time, and the changes can affect global surface temperature. But long-term changes over the period of human-caused global warming are minimal.
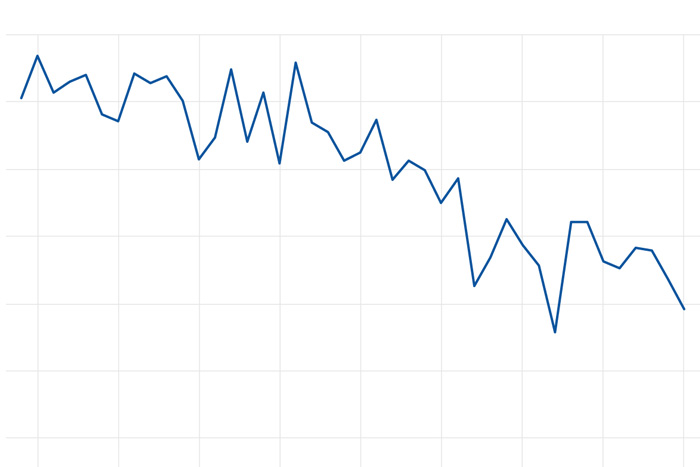
The amount of sea ice that survives the Arctic summer has declined by 13 percent per decade since the start of the 43-year satellite record.
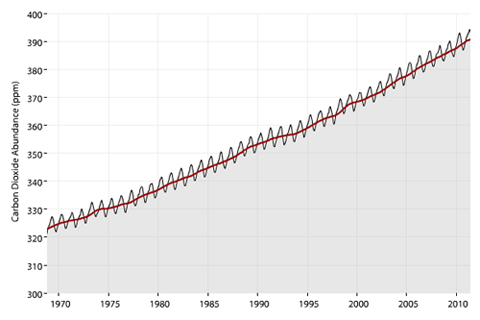
In the past 60 years, carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased 100-200 times faster than it did during the end of the last ice age.
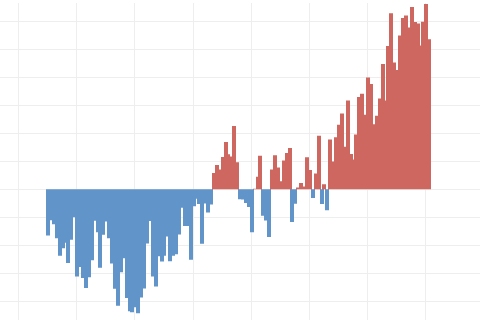
Earth's surface temperature has risen about 2 degrees Fahrenheit since the start of the NOAA record in 1850. It may seem like a small change, but it's a tremendous increase in stored heat.
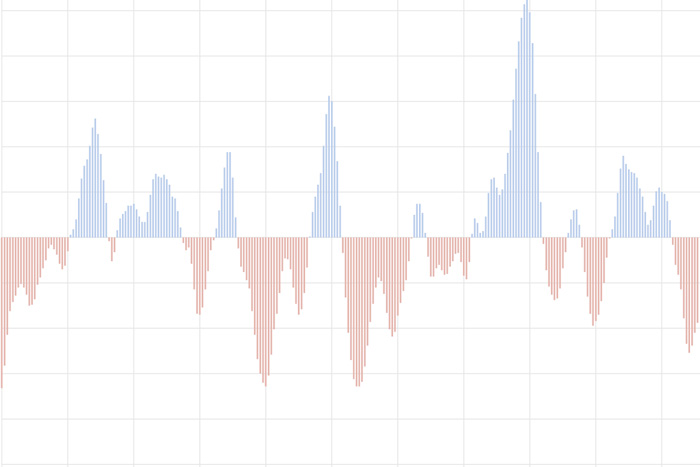
The Oceanic Nino Index tracks the sea surface temperature in the east-central tropical Pacific Ocean. It is NOAA's primary indicator of the climate patterns known as El Niño and La Niña.
From football games to concerts, planning for outdoor events increasingly demands a strategy for reducing heat-related risks.
NOAA and NOAA-funded researchers are looking at extreme rain events from many different angles to identify new sources of predictability. The goal is to one day be able to predict such events weeks or months in advance.
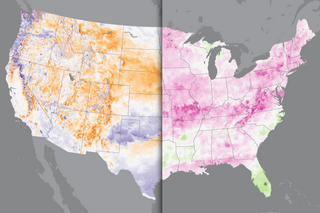
Forecasters think the climate system is poised to bring most of the U.S. a warmer-than-average June, and little drought relief is likely across the West.